Secure webhooks
Middesk supports three approaches to verify that webhook notifications are authentic and originate from Middesk.
Verify signatures
Middesk signs webhook requests by including a signature in the X-Middesk-Signature-256 header. Verify this signature to confirm the request came from Middesk.
Always verify the HMAC signature against the raw request body before parsing it as JSON. Parsing can alter the byte sequence (encoding changes, JSON reformatting, whitespace trimming), causing signature verification to fail. Only parse verified payloads.
Set up signature verification
Before you can verify signatures, define a secret using the Webhooks API.
Middesk generates signatures using HMAC with SHA-256.
Verify the signature in your webhook endpoint
- Extract the signature from the
X-Middesk-Signature-256header. - Compute an HMAC with SHA-256 using your secret as the key and the raw request body as the message.
- Compare the header signature to your computed signature using a constant-time comparison method.
Use Mutual TLS
The second way to authenticate webhook notifications is to verify Middesk’s client certificate during the TLS handshake.
In standard TLS, only the server presents a certificate. With Mutual TLS, the client (Middesk) also presents a certificate. Configure your server to request and verify this client certificate during the TLS handshake.
Verify Middesk’s certificate
Middesk’s webhook client certificate is issued by the DigiCert Assured ID Root G2 Certificate Authority. This CA is configured on most operating systems by default, or you can download it directly.
Verify the client certificate has these Subject Distinguished Name (Subject DN) fields:
These fields confirm the certificate was issued to Middesk, Inc. and is used for the intended purpose.
Configure reverse proxies
If you use a reverse proxy for TLS termination, configure it to request and verify the client certificate before routing requests to your backend. Verify the certificate subject matches the fields above before forwarding the request.
Use OAuth access tokens
A third, but most advanced, mechanism to authenticate webhook notifications is to use OAuth access tokens issued by your OpenID Connect Identity Provider. This method is best for enterprises with complex security requirements.
Use this method if:
- HMAC shared secrets don’t meet your security requirements. Your organization prohibits sharing secrets externally.
- Mutual TLS is incompatible with your infrastructure. Your edge proxies don’t support client certificate authentication or make it difficult to relay certificate information to backend applications.
- You need separation of security responsibilities. Security teams manage the Identity Provider while application teams focus on token verification.
- You require precise token scoping. Tokens can be scoped to specific resource URIs.
- You must comply with internal governance. Your organization requires internal IdP-issued tokens for all integrations.
How OAuth authentication works
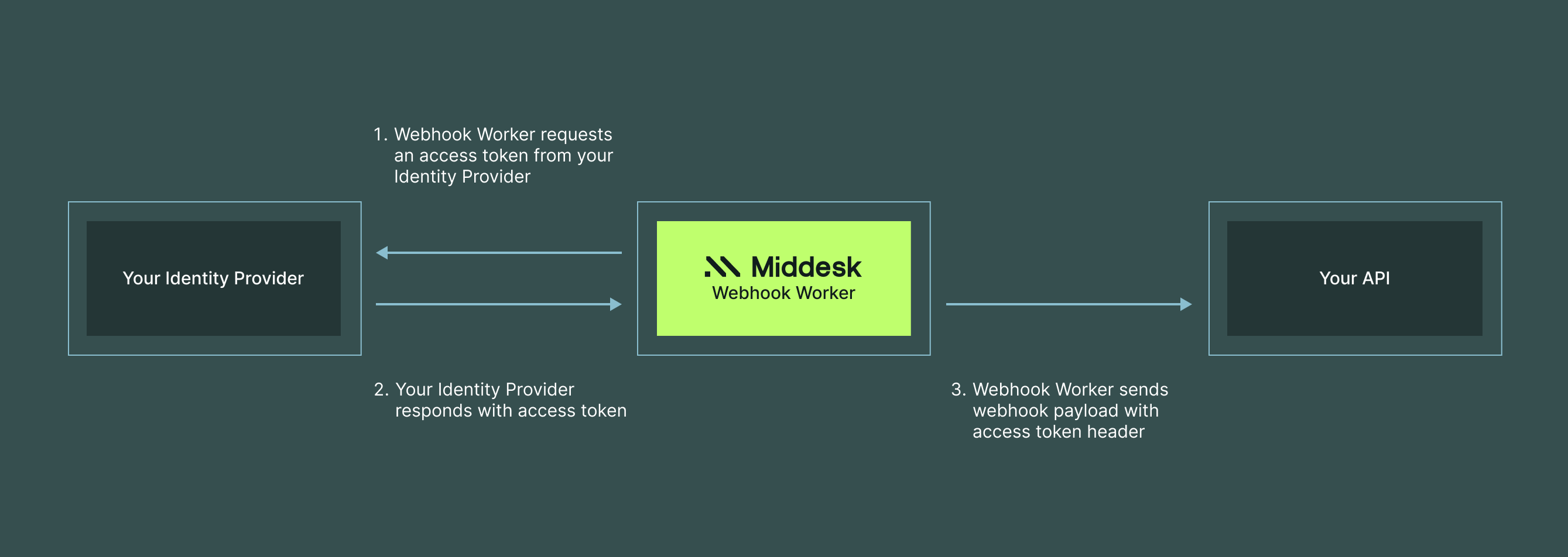
Token request
Middesk’s webhook worker requests an access token from your Identity Provider (IdP) by sending credentials and the specified scope (your webhook endpoint URI) to the token endpoint.
Refer to your internal documentation for token validation specifics.
Set up OAuth authentication
Register Middesk with your Identity Provider (IdP)
-
Register an application representing Middesk’s webhook worker.
-
Provide Middesk’s JWK Set URL:
https://api.middesk.com/v1/webhooks/oidc_keysYour IdP uses this URL to validate Middesk’s authentication credentials.
-
Save the generated Client ID.
Specify your API resource URI
Provide the URI of your API endpoint that receives webhook events. Middesk includes this URI in token requests to scope the access token.
Configure webhooks to use OAuth
After completing the setup, configure your webhook to use OAuth access tokens via the API. Include these four fields when creating or updating a webhook (currently not available in the Webhooks UI):